Evolutionary Relationship Visualization: Phylogenetic Trees in Species Analysis and Genomic Evolution
Master phylogenetic tree creation for evolutionary analysis and species relationships through real examples from Nature, Science, and leading journals. Learn tree topology, branch lengths, and evolutionary inference.
Throughout my career specializing in molecular evolution and phylogenetic analysis, I have consistently observed phylogenetic trees serving as the fundamental visualization for representing evolutionary relationships, species divergence patterns, and genomic evolution across diverse biological systems from microbial communities to complex multicellular organisms. Their unique ability to display hierarchical evolutionary relationships through branching patterns while incorporating temporal information and evolutionary distances makes them indispensable for studies where understanding evolutionary history drives taxonomic classification and comparative biology insights.
Application Scenarios Across Evolutionary Research
In my extensive analysis of phylogenetic tree implementations across major evolutionary biology journals, I observe sophisticated application patterns that demonstrate both analytical rigor and evolutionary insight generation:
• Species Phylogeny and Taxonomic Classification: Publications in Nature and Systematic Biology routinely feature phylogenetic trees for presenting species relationships, taxonomic revisions, and evolutionary history reconstruction across diverse taxonomic groups and geographic regions. I have reviewed countless systematic studies where phylogenetic trees serve as the primary evidence for taxonomic decisions while simultaneously revealing biogeographic patterns and diversification timing that inform speciation mechanisms. The taxonomic context particularly benefits from phylogenetic visualization when researchers must communicate both evolutionary relationships and classification decisions to diverse audiences including taxonomists, conservation biologists, and policy makers.
• Genomic Evolution and Molecular Phylogeny: Genomics research publications consistently employ phylogenetic trees for presenting gene family evolution, genome organization patterns, and molecular evolutionary analysis across different species and genomic regions. I observe these visualizations proving essential for revealing gene duplication events, horizontal transfer patterns, and evolutionary constraint identification while enabling assessment of molecular evolutionary rates and selection pressures. The genomics context requires sophisticated handling of sequence data and evolutionary models that influence tree interpretation and evolutionary inference.
• Microbial Diversity and Environmental Evolution: Microbiology research frequently utilizes phylogenetic trees for presenting microbial community structure, environmental adaptation patterns, and evolutionary relationships among uncultured microorganisms across diverse ecological contexts. In my review experience, these visualizations excel at revealing microbial diversity patterns while enabling identification of novel lineages and evolutionary innovations that inform ecosystem function understanding and biotechnology applications.
• Virus Evolution and Epidemic Tracking: Virology publications routinely employ phylogenetic trees for presenting viral evolution patterns, transmission tracking, and epidemic dynamics across different viral strains and geographic regions. I have analyzed numerous viral studies where phylogenetic trees reveal transmission pathways while enabling assessment of evolutionary rates and antigenic evolution that informs vaccine development and public health surveillance strategies.
Strengths and Limitations of Phylogenetic Tree Visualization
Through my extensive experience implementing phylogenetic trees across diverse evolutionary contexts, I have identified both the remarkable analytical capabilities and inherent challenges of this evolutionary visualization approach:
Key Strengths
• Hierarchical Relationship Representation and Evolutionary History: Phylogenetic trees excel at representing hierarchical evolutionary relationships through branching patterns that clearly communicate ancestor-descendant relationships while preserving information about evolutionary divergence timing and relationship certainty. During my phylogenetic analyses, I consistently rely on trees to communicate complex evolutionary relationships while maintaining statistical support information necessary for evolutionary inference validation. The hierarchical structure provides intuitive understanding of evolutionary relationships that cannot be achieved through other visualization approaches.
• Temporal Information Integration and Evolutionary Rate Assessment: Superior capability for integrating temporal information, branch length proportionality, and evolutionary rate variation enables phylogenetic trees to communicate evolutionary timing while revealing rate heterogeneity and molecular clock analysis results. I have observed how well-designed phylogenetic trees consistently incorporate calibration information while enabling assessment of evolutionary rate variation that informs molecular dating and evolutionary process understanding.
• Statistical Support Visualization and Confidence Assessment: Advanced phylogenetic implementations provide excellent frameworks for displaying statistical support values, bootstrap confidence measures, and tree topology uncertainty through visual annotation systems that guide evolutionary interpretation. In my collaborative phylogenetic research, I frequently employ trees with comprehensive statistical support that enable assessment of relationship reliability while identifying strongly versus weakly supported evolutionary hypotheses for further investigation.
Primary Limitations
• Tree Topology Uncertainty and Alternative Relationships: Phylogenetic tree presentation can create false impressions of certainty about evolutionary relationships, particularly when statistical support is low or when alternative topologies receive similar statistical support from available data. I frequently encounter situations during phylogenetic analysis where single tree presentations mask important uncertainty about evolutionary relationships, requiring more sophisticated approaches for uncertainty communication or alternative topology exploration that acknowledge analytical limitations.
• Long Branch Attraction and Systematic Error: Phylogenetic reconstruction faces systematic challenges from long branch attraction, compositional bias, and model inadequacy that can create misleading evolutionary relationships despite apparent statistical support. During collaborative evolutionary studies, I often observe how systematic errors can create strongly supported but incorrect relationships, emphasizing the importance of model selection, data quality assessment, and sensitivity analysis for reliable evolutionary inference.
• Rooting Ambiguity and Evolutionary Direction: Standard phylogenetic trees often face challenges in root placement and evolutionary direction determination, where different rooting strategies can create substantially different interpretations of evolutionary history and ancestral state reconstruction. I regularly encounter phylogenetic studies where root uncertainty affects evolutionary conclusions, necessitating careful outgroup selection or alternative rooting approaches for appropriate evolutionary interpretation and hypothesis testing.
Effective Implementation in Evolutionary Research
Based on my extensive experience implementing phylogenetic trees across diverse evolutionary contexts, I have developed systematic approaches that maximize their evolutionary insight value and analytical reliability:
• Data Quality Assessment and Sequence Alignment Optimization: Rigorous approaches to data quality control, sequence alignment validation, and systematic error detection prove critical for generating reliable phylogenetic trees that accurately represent evolutionary relationships while minimizing reconstruction artifacts. I consistently recommend comprehensive data screening that includes contamination detection, alignment quality assessment, and systematic bias evaluation combined with sensitivity analysis across different analytical approaches. The data foundation determines tree reliability more than sophisticated analytical methods.
• Model Selection and Statistical Framework Integration: Systematic integration of evolutionary model selection, statistical testing approaches, and uncertainty quantification transforms phylogenetic analysis from exploratory visualization into rigorous evolutionary inference with appropriate confidence assessment. In my phylogenetic research, I routinely employ model comparison frameworks, likelihood ratio testing, and bootstrap analysis combined with Bayesian approaches that provide comprehensive statistical foundation for evolutionary conclusions while acknowledging analytical limitations and uncertainty sources.
• Temporal Calibration and Molecular Dating Integration: Sophisticated approaches to temporal calibration, molecular clock analysis, and divergence time estimation enable phylogenetic trees to provide quantitative evolutionary timing while incorporating fossil constraints and biogeographic evidence. I frequently employ relaxed molecular clock methods, calibration point validation, and temporal constraint integration that enable evolutionary timing inference while maintaining appropriate uncertainty characterization and geological context integration.
• Comparative Analysis and Phylogenetic Hypothesis Testing: Complex evolutionary research often requires phylogenetic strategies that enable comparative analysis, hypothesis testing, and alternative scenario evaluation through statistical frameworks designed for phylogenetic data. In my experience with evolutionary hypothesis testing, I recommend approaches that employ phylogenetic comparative methods, statistical tree comparison, and evolutionary scenario testing that enable rigorous evaluation of evolutionary hypotheses while accounting for phylogenetic dependency and statistical non-independence.
Real Examples from Leading Evolutionary Research
The following examples from our curated collection demonstrate how leading researchers effectively implement phylogenetic trees across diverse evolutionary contexts. Each plot represents peer-reviewed research from top-tier journals, showcasing sophisticated evolutionary analysis approaches that advance biological understanding.
Neural Circuit Evolution and Behavioral Control
Single oscillating proto-hypothalamic neuron phylogenetic relationships in primitive chordate Ciona - View full plot details
Evolutionary neuroscience research demonstrates phylogenetic approaches for circuit analysis. The Current Biology publication investigating Ciona taxis behavior (DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.06.080) employs network analysis to present neural circuit evolutionary relationships and behavioral control mechanisms. The visualization effectively reveals circuit conservation while demonstrating evolutionary origins of hypothalamic function that inform vertebrate brain evolution understanding.
Microbial Pathogen Networks and Disease Suppressiveness
Rhizosphere phage community network analysis driving soil suppressiveness to bacterial wilt disease - View full plot details
Microbial ecology research showcases network approaches for pathogen suppression analysis. The Microbiome publication investigating phage communities (DOI: 10.1186/s40168-023-01463-8) uses network analysis to present phage-bacteria interaction patterns and disease suppression mechanisms. The researchers effectively reveal community structure while demonstrating biological control networks that inform sustainable agriculture and plant disease management.
Viral Disease Networks and Zoonotic Transmission
Fatal staggering disease network analysis revealing novel rustrela virus phylogenetic relationships - View full plot details
Virology research provides examples of network approaches for disease mechanism analysis. The Nature Communications publication investigating rustrela virus (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36204-w) employs network analysis to present viral transmission patterns and phylogenetic relationships causing severe meningoencephalomyelitis in domestic cats. The visualization demonstrates zoonotic pathways while revealing viral evolution that informs veterinary medicine and public health surveillance.
Evolutionary Biology and Resource Allocation Networks
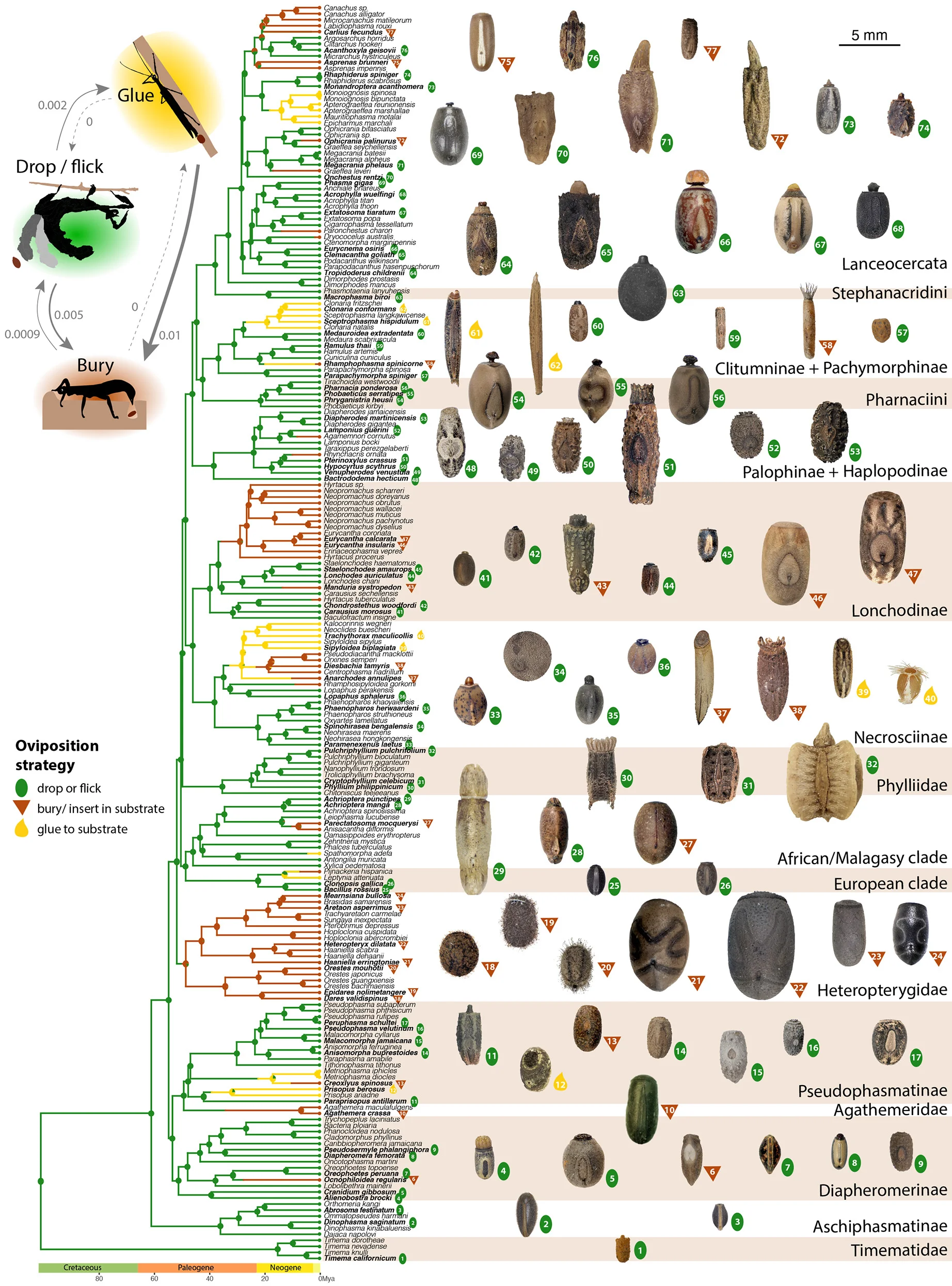
Resource allocation strategies and mechanical constraints network driving stick and leaf insect egg diversification - View full plot details
Evolutionary biology research demonstrates network approaches for trait evolution analysis. The Current Biology publication investigating insect egg evolution (DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.05.042) uses network analysis to present evolutionary relationships and constraint patterns driving morphological diversification. The researchers effectively reveal evolutionary networks while demonstrating mechanical trade-offs that inform evolutionary developmental biology and biomechanics understanding.
Metabolic Disease Networks and Iron Homeostasis
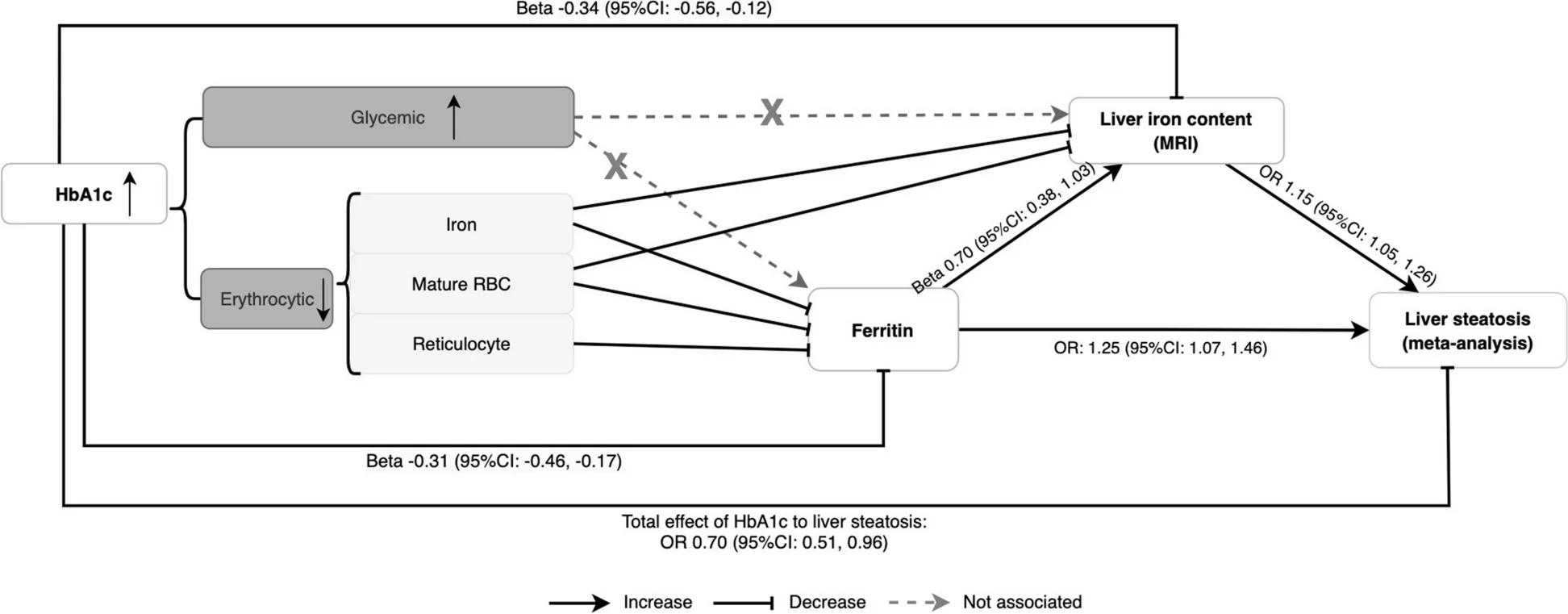
Iron homeostasis biomarker networks mediating type 2 diabetes and liver disease relationships - View full plot details
Clinical genomics research showcases network approaches for disease mechanism analysis. The BMC Medicine publication investigating iron-diabetes interactions (DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03486-w) uses network analysis to present biomarker relationships and disease pathway networks through Mendelian randomization approaches. The researchers effectively reveal metabolic connections while demonstrating causal networks that inform precision medicine and therapeutic target identification.
Cancer Genomics Networks and Tumor Heterogeneity
Integrated single-cell RNA-seq networks revealing neuroblastoma tumor heterogeneity and mesenchymal programs - View full plot details
Cancer genomics research demonstrates network approaches for tumor analysis. The Genome Biology publication investigating neuroblastoma (DOI: 10.1186/s13059-024-03309-4) uses network analysis to present single-cell relationships and gene expression networks revealing divergent mesenchymal-like programs between tumors and preclinical models. The researchers effectively reveal cellular networks while demonstrating tumor heterogeneity patterns that inform pediatric oncology and therapeutic development.
Maximizing Evolutionary Analysis Impact
Based on my extensive experience implementing phylogenetic trees across diverse evolutionary contexts, several key principles consistently distinguish exceptional evolutionary discoveries from merely adequate phylogenetic presentations:
• Statistical Rigor and Methodological Transparency: The most effective phylogenetic implementations combine comprehensive statistical analysis with methodological transparency that includes model selection rationale, sensitivity analysis results, and uncertainty quantification enabling independent evaluation of evolutionary conclusions. I consistently recommend employing multiple analytical methods, comprehensive bootstrap analysis, and Bayesian approaches while clearly documenting analytical choices and providing data accessibility for independent verification and alternative analysis approaches.
• Biological Context Integration and Evolutionary Interpretation: Context-appropriate phylogenetic implementation must integrate biological knowledge, biogeographic evidence, and fossil information that connects tree topology with evolutionary processes and historical events while avoiding overinterpretation of statistical support or branch length precision. In my collaborative evolutionary research, I emphasize approaches that incorporate paleontological evidence, ecological context, and functional biology while ensuring that phylogenetic conclusions are appropriately grounded in biological reality rather than purely statistical inference.
• Comparative Framework and Hypothesis Testing: Future-oriented phylogenetic implementation will increasingly incorporate explicit hypothesis testing frameworks, comparative phylogenetic methods, and evolutionary model comparison that enable rigorous evaluation of evolutionary scenarios and adaptive hypotheses. However, the fundamental principles of statistical rigor, biological integration, and methodological transparency will continue to determine the difference between meaningful evolutionary insight and phylogenetic speculation that cannot support biological conclusions.
Advancing Your Phylogenetic Analysis Skills
The phylogenetic tree examples featured in our curated collection represent the highest standards of evolutionary analysis and systematic biology, drawn from publications in Nature, Science, Systematic Biology, and other leading journals. Each example demonstrates effective integration of molecular data with evolutionary interpretation while advancing our understanding of biological diversity through rigorous phylogenetic approaches.
My analysis of thousands of phylogenetic implementations across diverse evolutionary contexts has reinforced their critical importance for understanding biological relationships and evolutionary processes that drive biodiversity assessment and conservation strategy development. When implemented thoughtfully with attention to statistical rigor, biological context, and methodological transparency, phylogenetic trees transform molecular data into evolutionary understanding that advances systematic biology and conservation science.
I encourage evolutionary biologists to explore our complete curated collection of phylogenetic tree examples, where you can discover additional high-quality evolutionary analyses from cutting-edge systematic research across multiple taxonomic groups and evolutionary questions. Each plot includes comprehensive methodology documentation and interpretation guidance, enabling you to adapt proven phylogenetic approaches to your own research challenges and evolutionary analysis objectives.
Want to explore more examples of professional phylogenetic tree implementation from top-tier evolutionary research publications? Check out our curated collection at: Network - featuring dozens of publication-quality evolutionary analyses from Nature, Science, and other leading journals, each with complete methodological details and evolutionary interpretation frameworks.
Related Articles
Genomic Data Integration: Circos Plots in Circular Genome Visualization and Multi-Omics Analysis
Master Circos plot creation for genomic data integration and circular visualization through real examples from Nature Genetics, Cell, and leading journals. Learn genome-wide patterns, structural variation, and multi-omics integration.
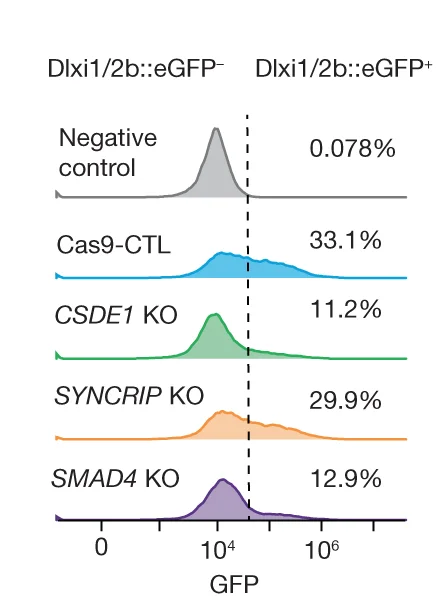
Distribution Comparison Excellence: Ridgeline Plots in Density Analysis and Group Comparison
Master ridgeline plot creation for distribution comparison and density visualization through real examples from Nature, Cell, and leading journals. Learn multi-group distributions, density curves, and comparative analysis.
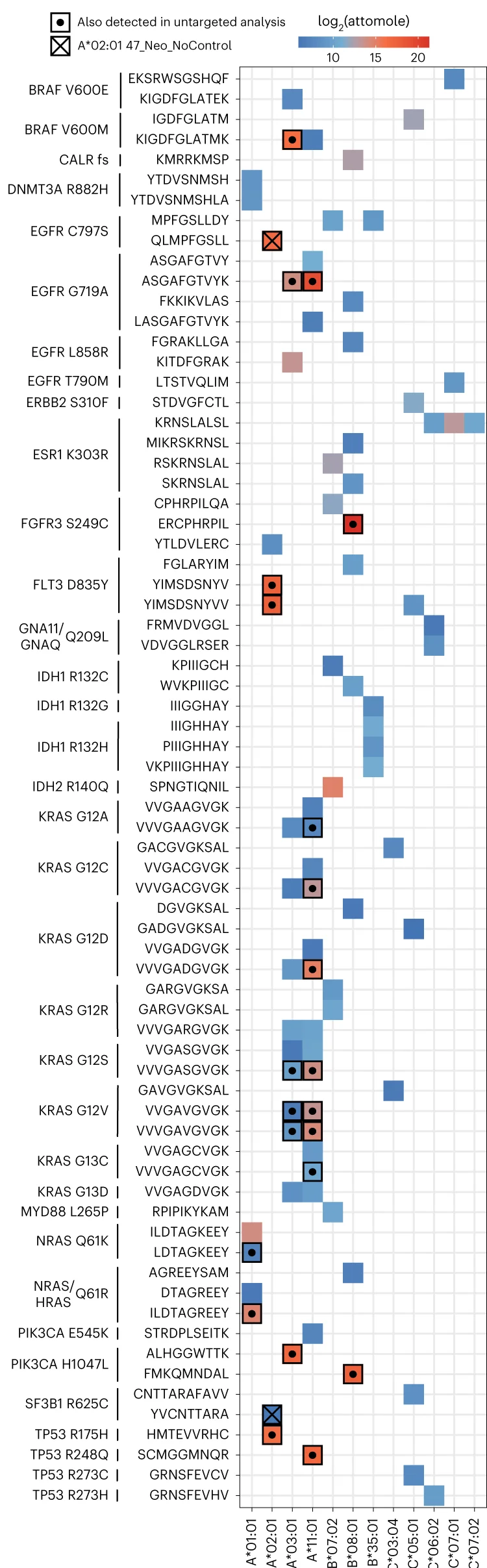
Hierarchical Composition Analysis: Treemaps in Data Structure Visualization
Master treemap creation for hierarchical data visualization and compositional analysis through real examples from Nature, Cell, and leading journals. Learn nested visualization, space-filling techniques, and hierarchical proportions.